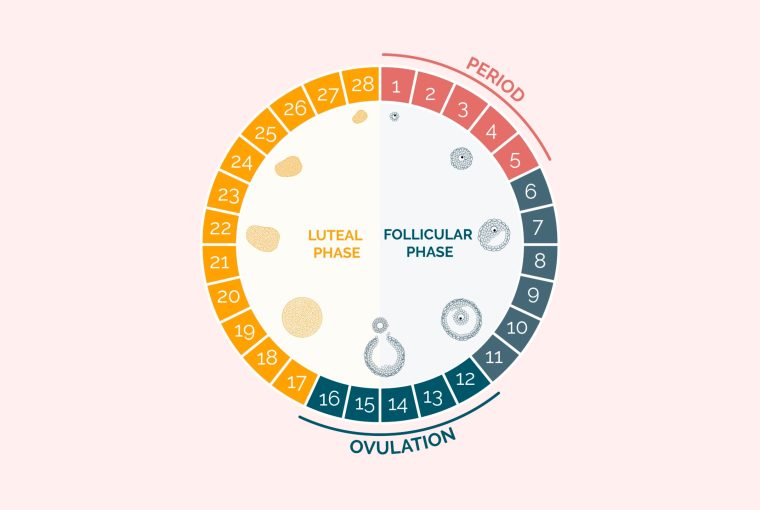
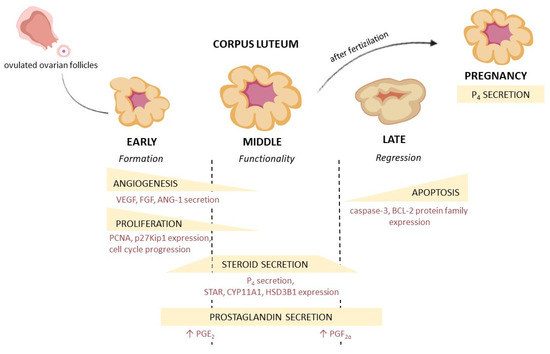
The corpus luteum is a small gland of great importance because its proper functioning determines not only the appropriate course of the estrous/menstrual cycle and embryo implantation, but also the subsequent maintenance of pregnancy. Among the well-known regulators of luteal tissue functions, increasing attention is focused on the role of neuropeptides and adipose tissue hormones—adipokines. Growing evidence points to the expression of these factors in the corpus luteum of women and different animal species, and their involvement in corpus luteum formation, endocrine function, angiogenesis, cells proliferation, apoptosis, and finally, regression. In the present review, we summarize the current knowledge about the expression and role of adipokines, such as adiponectin, leptin, apelin, vaspin, visfatin, chemerin, and neuropeptides like ghrelin, orexins, kisspeptin, and phoenixin in the physiological regulation of the corpus luteum function, as well as their potential involvement in pathologies affecting the luteal cells that disrupt the estrous cycle.
Cells, Free Full-Text, freecell online 100

An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system
ChIP analysis of histone modifications at the Ig e locus in CL-01
Frontiers The fragmentomic property of plasma cell-free DNA
Tarin-loaded nanoliposomes activate apoptosis & autophagy

Solved A cell-free extract of yeast known to contain all of
Cells, Free Full-Text, click desenvolvimento aec entrar

Cells, Free Full-Text, freecell online 100
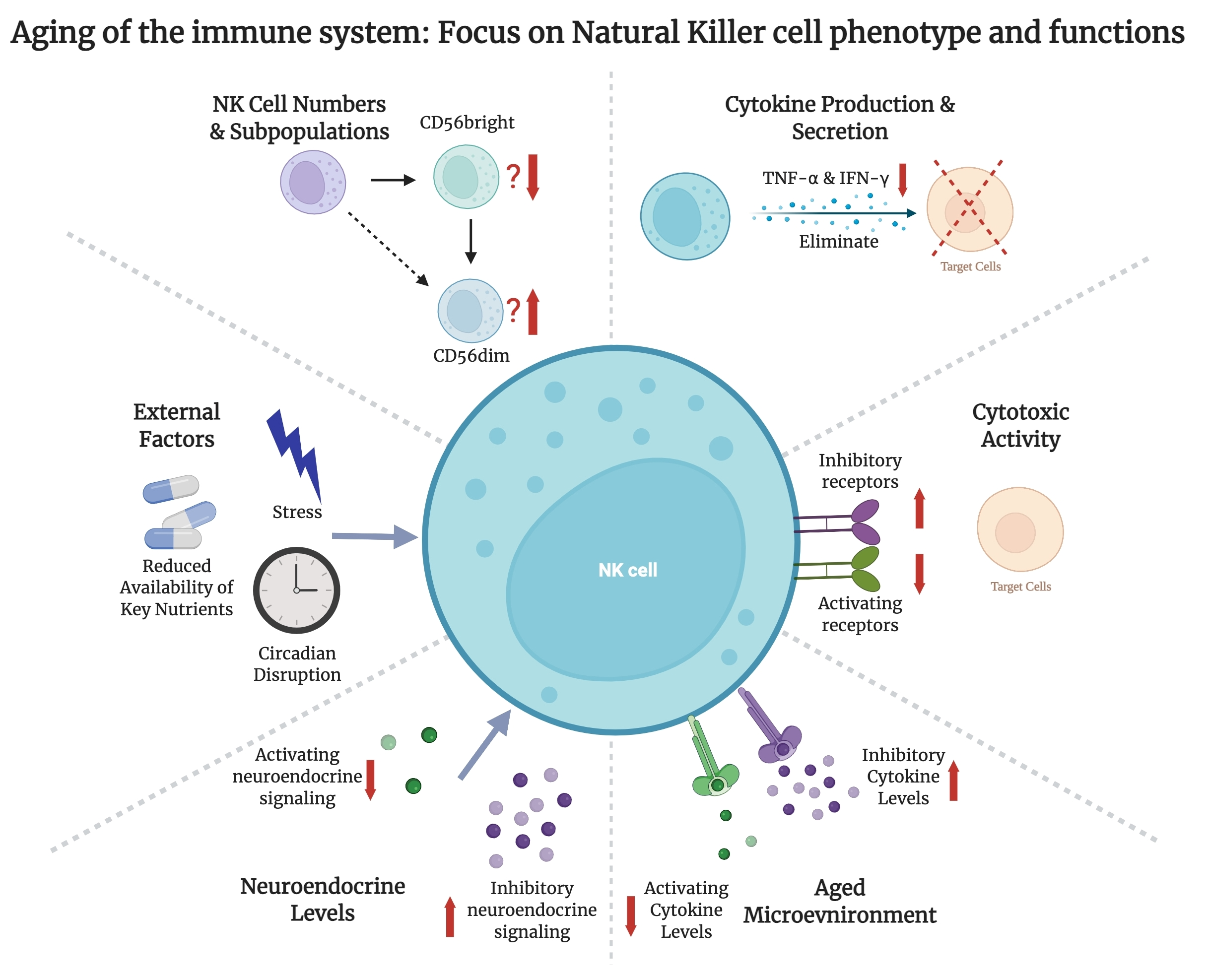
Cells, Free Full-Text
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology on X: From May cover

Advances and applications of cell-free systems for metabolic
FreeCell - Play Online & 100% Free
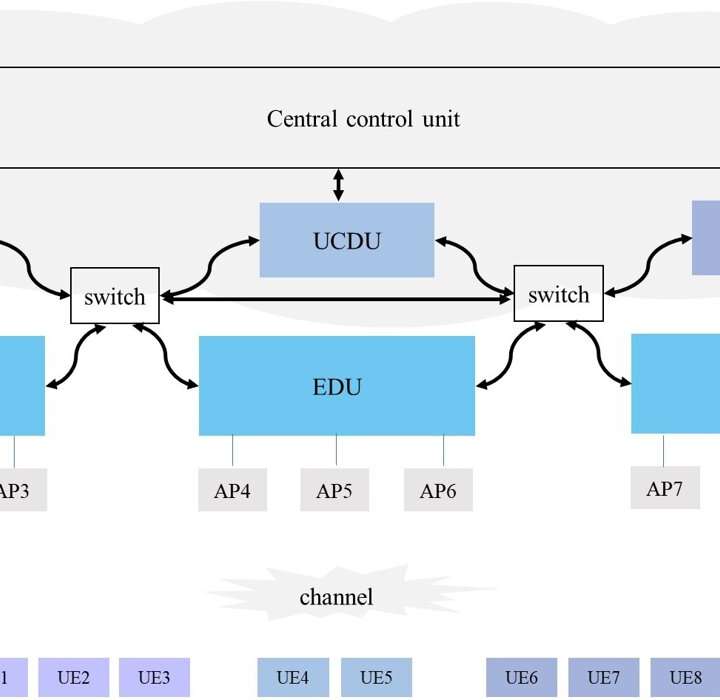
Full-spectrum cell-free RAN for 6G systems: System design and
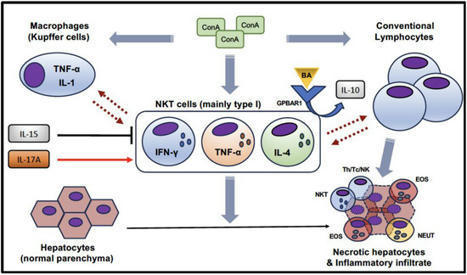
Pathogenesis of antineutrophil cytoplasmic auto

Early clinical experience using donor-derived cell-free DNA to