Seasonal and circadian genetic variation charted across the human body
4.5 (757) · $ 7.00 · In stock
The daily rotation of Earth and its yearly voyage around the sun marks the natural rhythm of life on the planet. Human health indicators such as body temperature, blood pressure and sleep, as well as animal behavior including foraging, molting, mating or hibernating, is influenced by innate biological clocks that work over circadian (day-night and twenty-four hour) and/or circannual (seasons and twelve-month) cycles.

Plants can be larks or night owls just like us

Centre for Genomic Regulation Website
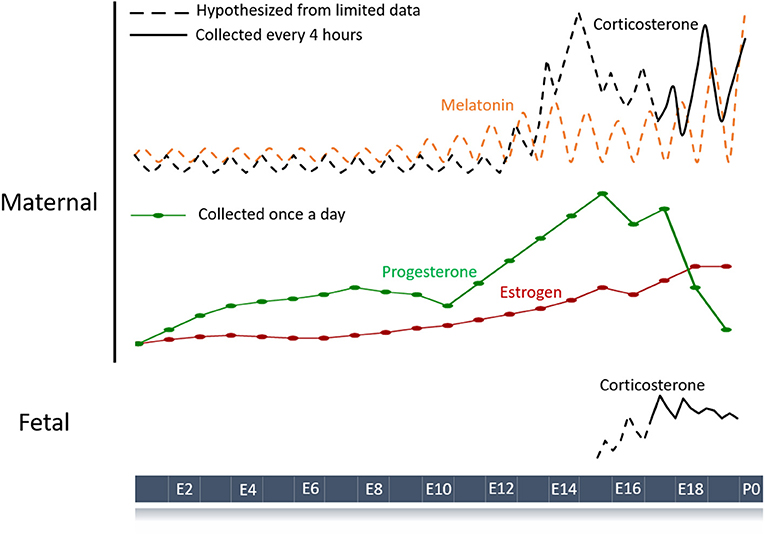
Frontiers Maternal-Fetal Circadian Communication During Pregnancy

Researchers uncover importance of aligning biological clock with day-night cycles

Modern Life Suppresses An Ancient Body Rhythm - The New York Times

Association between chronotype and cardio-vascular disease risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis - Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health

Reading your body clock with a molecular timetable, inspired by flowers
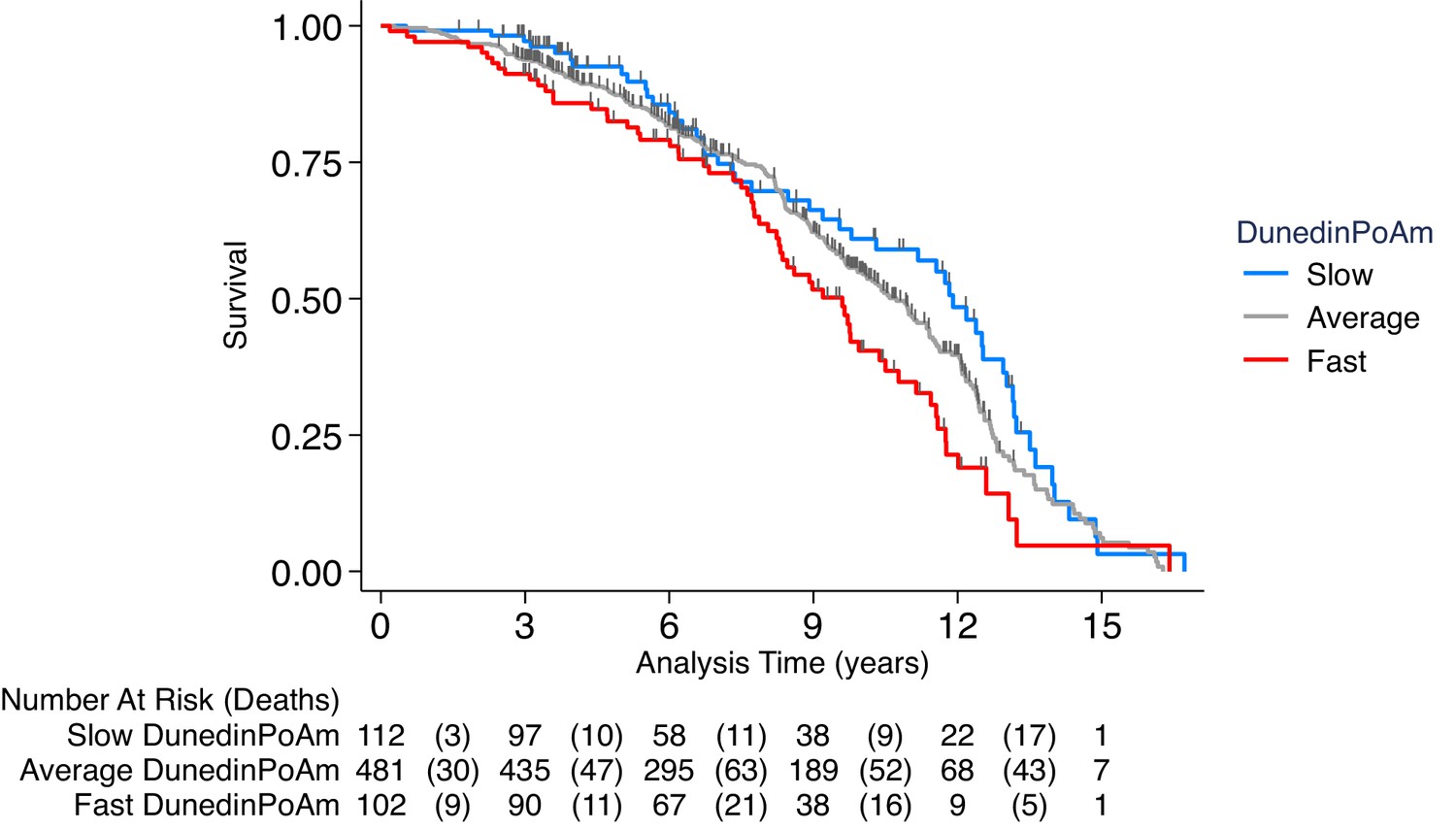
Quantification of the pace of biological aging in humans through a blood test, the DunedinPoAm DNA methylation algorithm

Seasonal regulation in the bean bug brain's biological clock

Circadian rhythmicity persists through the Polar night and midnight sun in Svalbard reindeer












