Skin tissue regeneration for burn injury
4.7 (228) · $ 29.99 · In stock
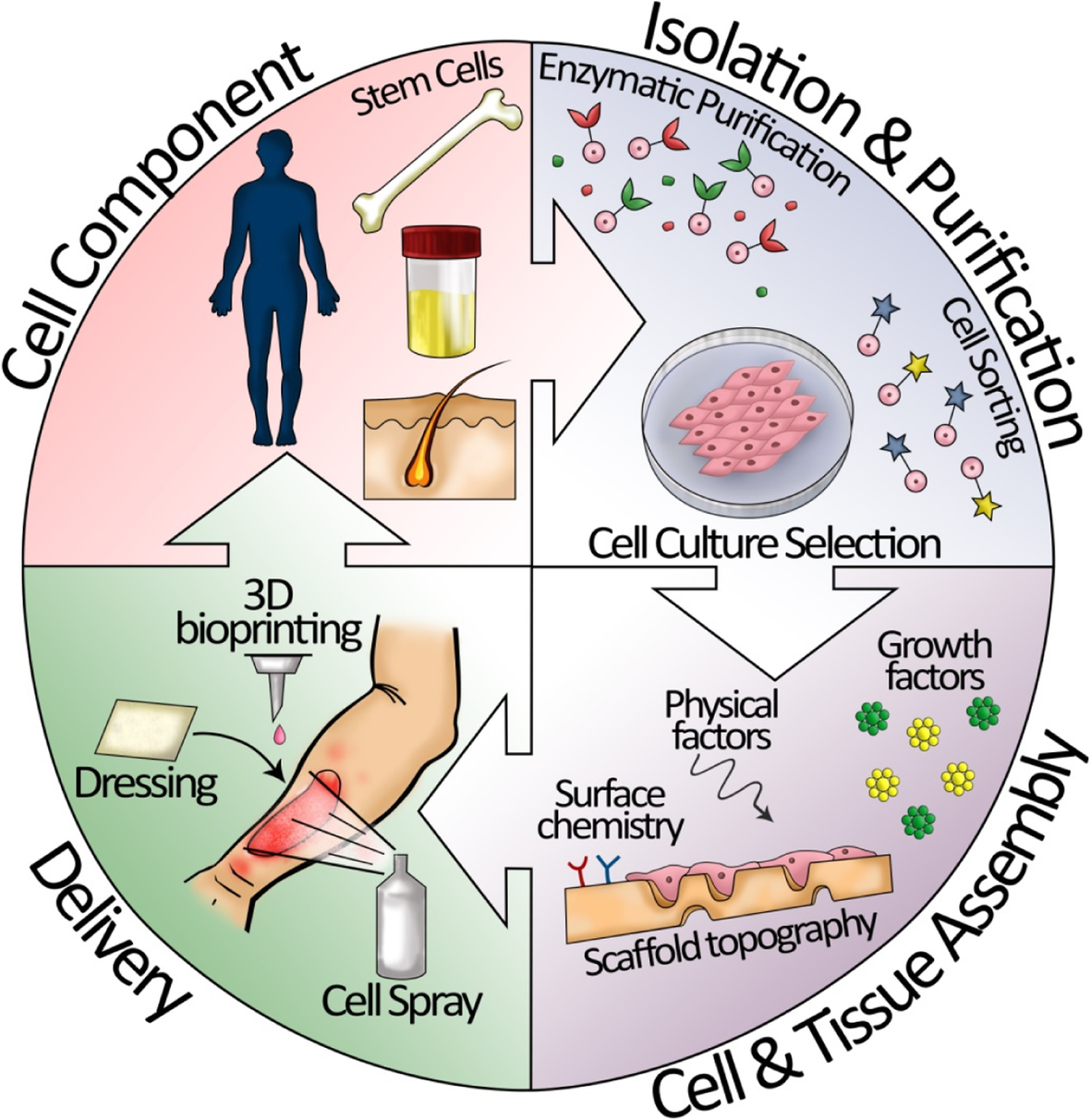
The skin is the largest organ of the body, which meets the environment most directly. Thus, the skin is vulnerable to various damages, particularly burn injury. Skin wound healing is a serious interaction between cell types, cytokines, mediators, the neurovascular system, and matrix remodeling. Tissue regeneration technology remarkably enhances skin repair via re-epidermalization, epidermal-stromal cell interactions, angiogenesis, and inhabitation of hypertrophic scars and keloids. The success rates of skin healing for burn injuries have significantly increased with the use of various skin substitutes. In this review, we discuss skin replacement with cells, growth factors, scaffolds, or cell-seeded scaffolds for skin tissue reconstruction and also compare the high efficacy and cost-effectiveness of each therapy. We describe the essentials, achievements, and challenges of cell-based therapy in reducing scar formation and improving burn injury treatment.

Burn Wounds - Medline Corius

Multifunctional hydrogels for chronic wounds repairing - Wang - Biosurface and Biotribology - Wiley Online Library

Biological properties and surgical applications of the human amniotic membrane. - Abstract - Europe PMC
IJMS, Free Full-Text

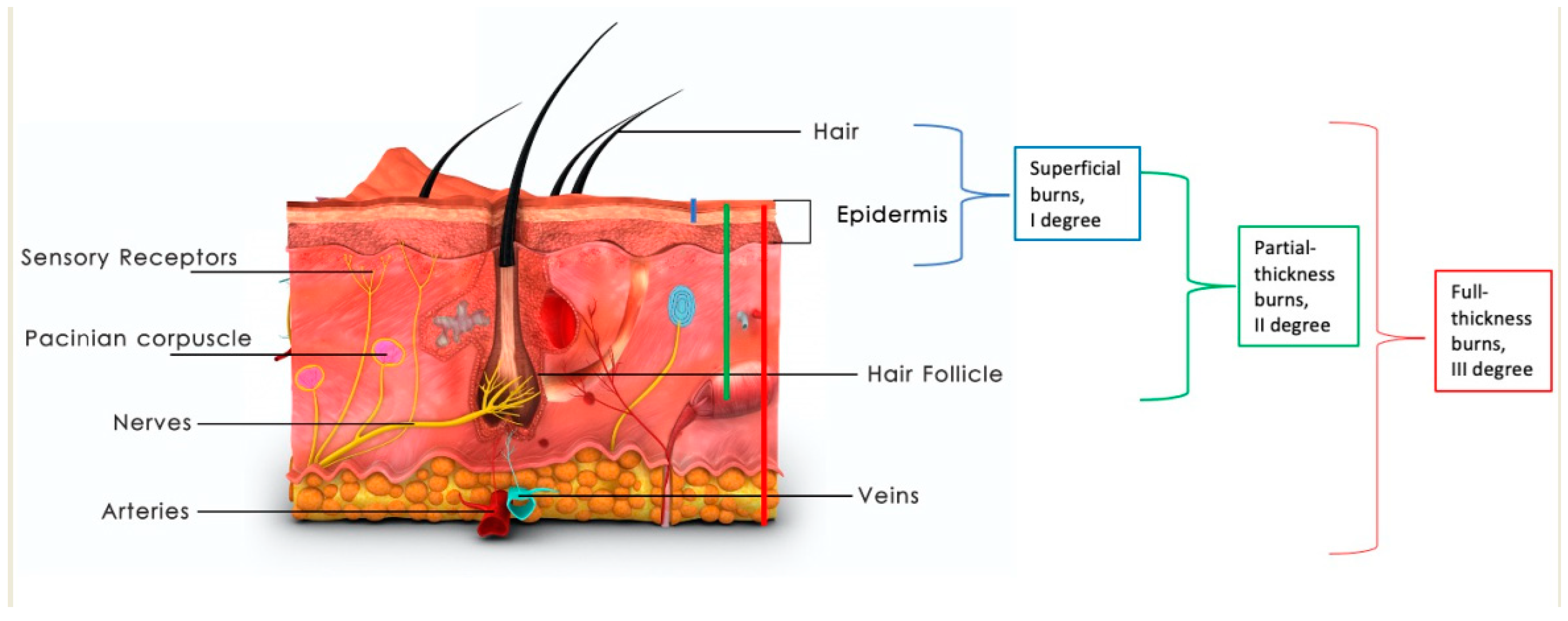
Skin regeneration, repair, and reconstruction: present and future
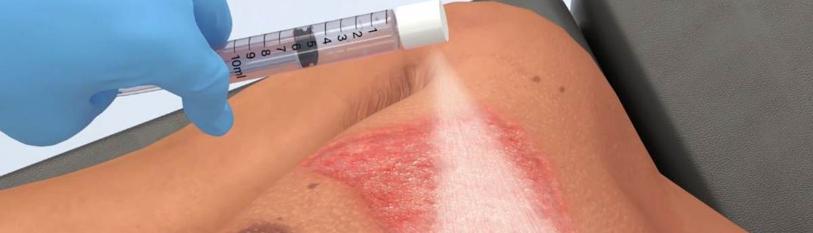
The Use of Human Stem Cells to Promote Tissue Healing in Skin Burn
How to Treat a Burn Injury

Introduction

Burn Wound Care Musculoskeletal Key
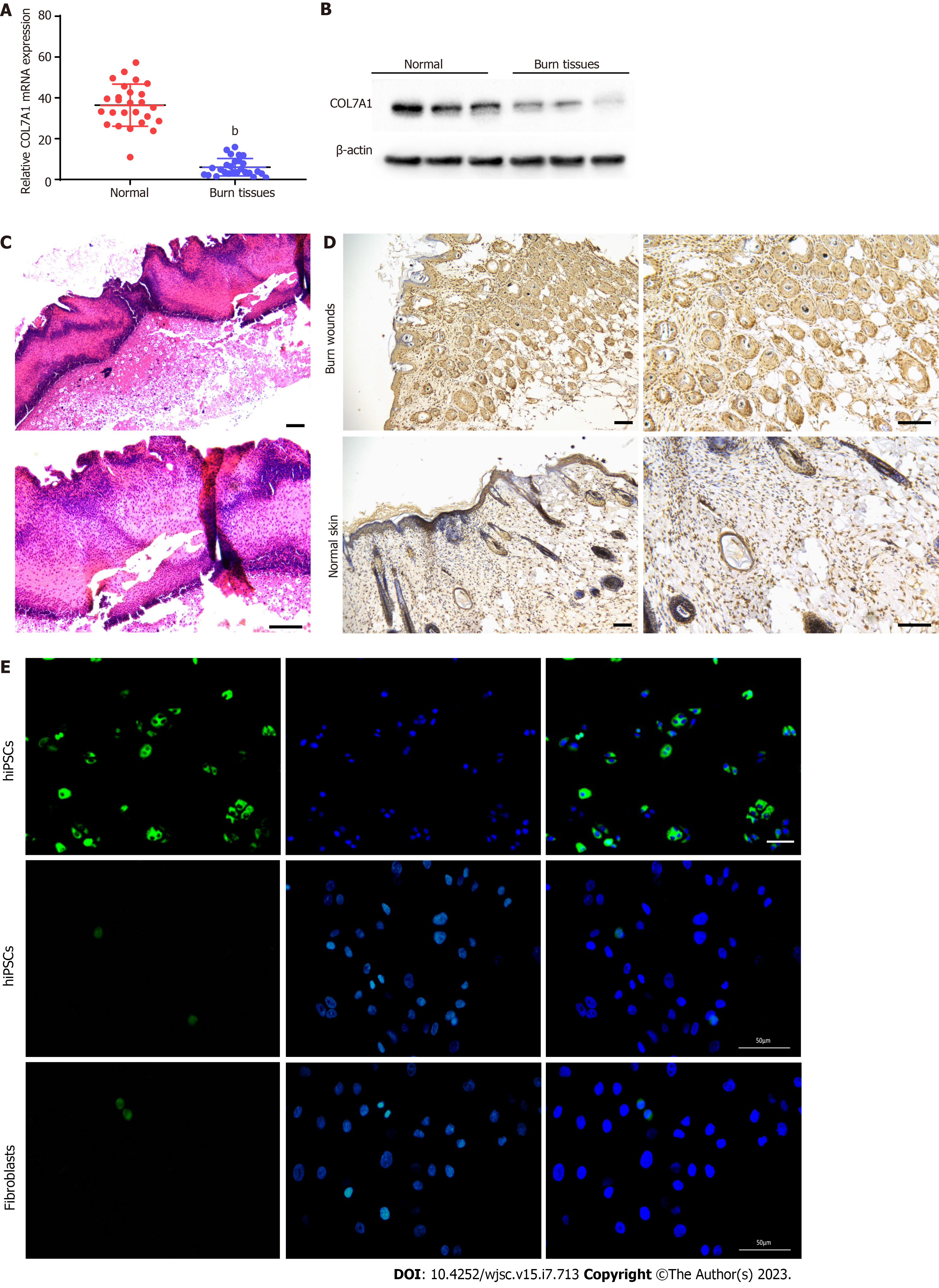
Transplantation of human induced pluripotent stem cell derived
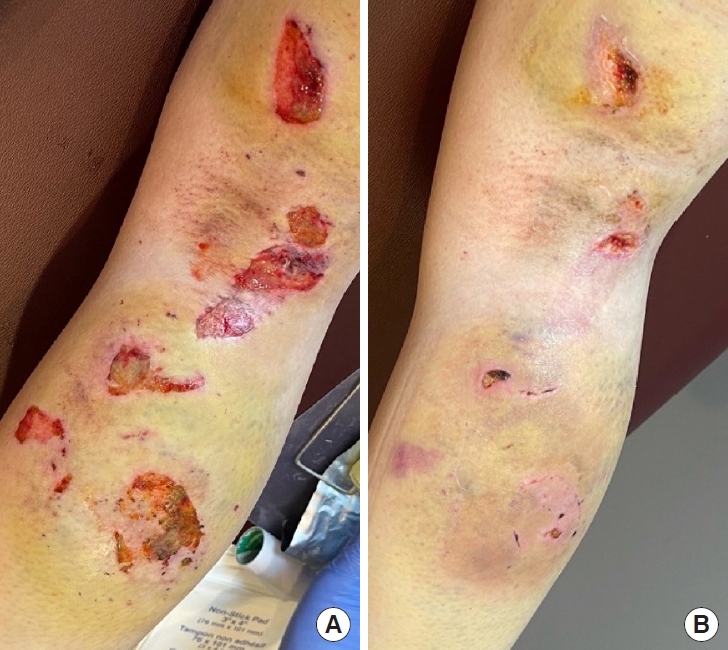
Topical Application of Purified Amniotic Fluid Accelerated Healing of Full-Thickness Burns, Negating the Need for Skin Grafts: A Case Report
Stem Cell Therapy for Burns: Story so Far. - Document - Gale Academic OneFile

Engineered artificial skins: Current construction strategies and
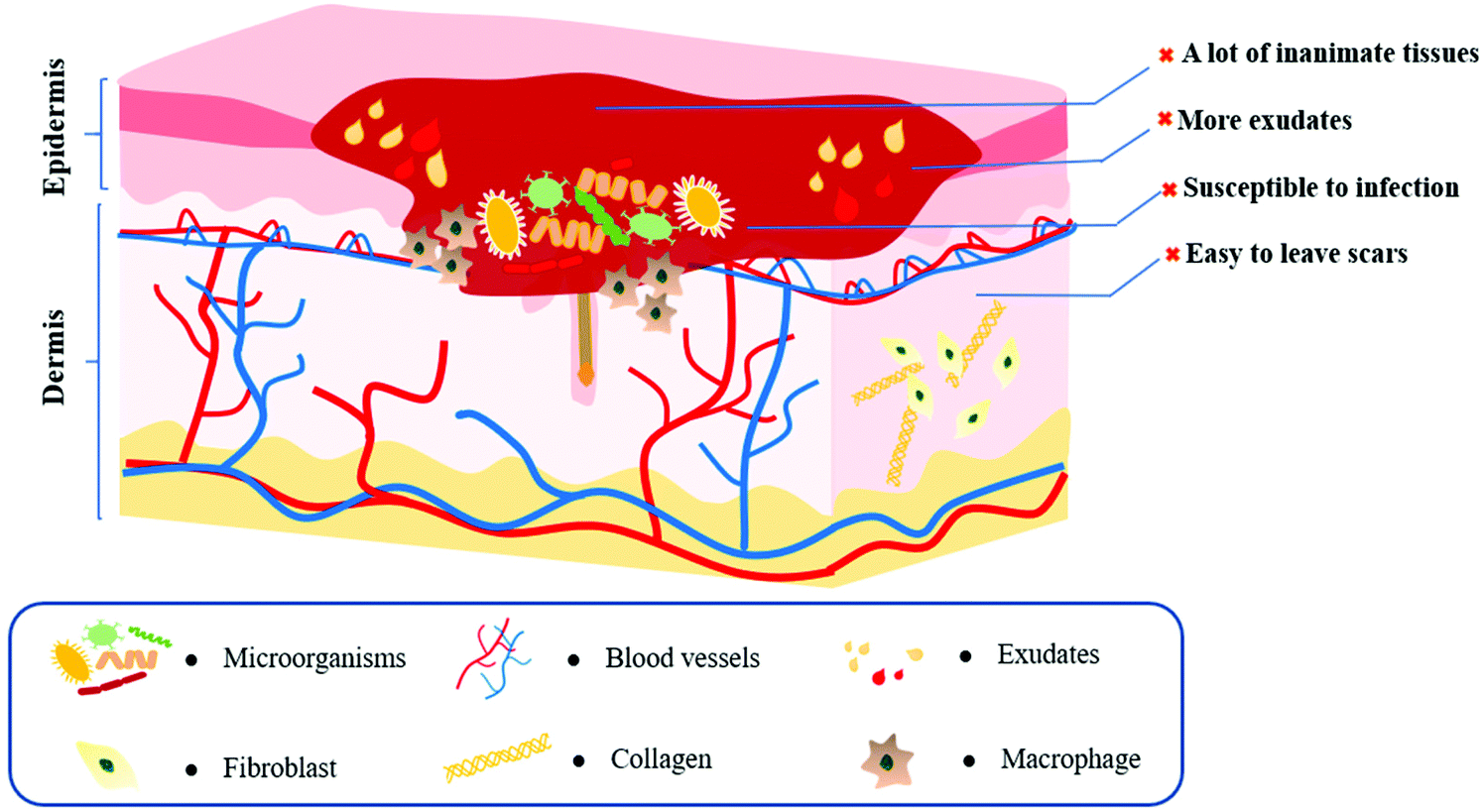
Recent trends on burn wound care: hydrogel dressings and scaffolds