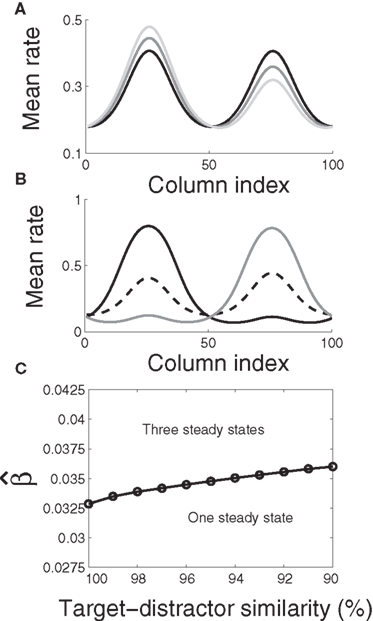
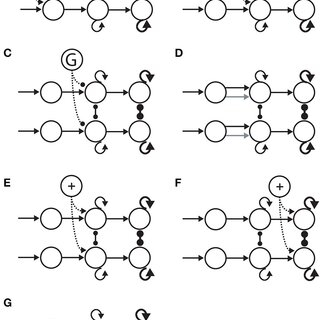
The steady states of the system. (A) The system (Equation 1) has
4.8 (250) · $ 21.50 · In stock

The steady states of the system. (A) The system (Equation 1) has one
Frontiers Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit

PDF) Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit
Michael C. Dorris's research works Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (CAS) and other places
Frontiers Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit

The steady states of the system. (A) The system (Equation 1) has one

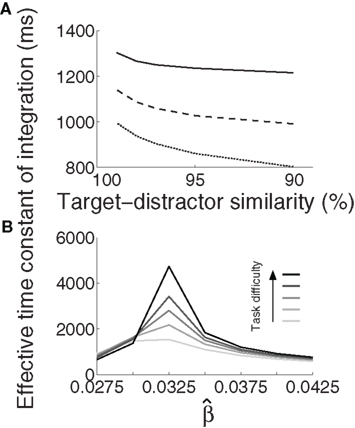
a and b. In figure a the estimated normal zone length between the
Frontiers Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit

PDF) Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit

PDF) Gain Modulation by an Urgency Signal Controls the Speed–Accuracy Trade-Off in a Network Model of a Cortical Decision Circuit

Dominic STANDAGE, Marie Curie Senior Research Fellow, PhD, Computer Science, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, School of Psychology